Payroll management, known in the United States as payroll management, is one of the most critical - and often most complex - aspects of any business operation. Whether your company has 3 employees or 300, paying salaries correctly is not only a legal obligation: it is a sign of responsibility, organization and respect for your team.
However, complying with all of the payroll tax, labor and administrative regulations can be a real challenge. From withholding taxes to employer contributions, mandatory forms and quarterly reporting, a single mistake can translate into IRS penalties, employment lawsuits or loss of internal confidence.
The truth is that payroll is not just about issuing checks or transfers. It involves understanding and correctly applying federal, state and local laws; keeping impeccable records; filing timely reports; and ensuring that each employee receives his or her due in form, substance and time.
In this article we will guide you through everything you need to know about payroll management in the U.S., with a practical approach adapted to the reality of small and medium-sized companies. We will analyze the legal obligations, the most common mistakes, the best practices, and how a specialized consultancy -like the one we offer at JJRB- can make the difference between precarious compliance and an efficient management that boosts your business.
Because paying well is more than just delivering: it is building trust, culture and growth.
And that all starts with understanding how to properly manage your payroll.
What exactly is payroll management and why is it so important for your business?
The payroll managment or payroll in the United States is not limited to issuing biweekly or monthly payments to your employees. It is a comprehensive system that involves accurate calculations, legal compliance, tax reporting and ongoing documentation. When managed correctly, it ensures that employees are paid on time and that the company complies with all labor and tax regulations.
What exactly does payroll management include?
- Calculation of gross and net salaries: It involves determining how much each employee has earned (hourly or fixed salary), including overtime, bonuses and commissions. Taxes, benefit contributions (health, pension, etc.) and other items are then deducted to obtain the net pay.
- Withholding and payment of taxes: The employer must withhold Federal Income Tax, Social Security, Medicare, and in many cases, state and local taxes. In addition, the employer must pay its share of certain tax liabilities.
- Tax returns and periodic reports: There are required forms such as Form 941 (quarterly), W-2 (annual for employees) and W-3 (summary of W-2s). State employment and unemployment reports must also be filed.
- Labor records and compliance: The Department of Labor requires detailed records of hours worked, pay, deductions and employee classifications (employee vs. contractor).
Why is it so important?
Because payroll not only affects cash flow and your team's morale. Poor management can lead to:
- IRS or Department of Labor Penalties for non-compliance or errors.
- Tax or labor auditswhich paralyze the operation and generate stress.
- Loss of employee confidencewhich can lead to high turnover and negative reputation.
- Legal problemssuch as claims for unpaid wages, misclassification errors, or union non-compliance.
Many small businesses make the mistake of treating payroll as a secondary administrative task. But a well managed payroll is a pillar of financial health and organizational culture.. If your employees trust that they will be paid correctly, they will be more motivated and engaged. And if the IRS trusts you to meet your obligations, you'll sleep better.
At JJRB, we help companies of all sizes implement clear, automated and fully compliant payroll systems. Because more than just paying salaries, it's about manage people and protect the operational heart of your business.
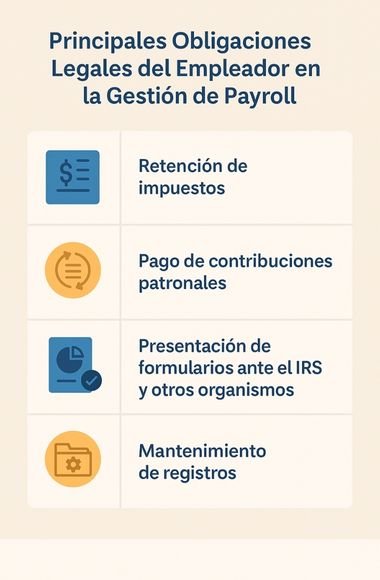
Employer's main legal obligations in payroll management
Managing payroll in the United States involves a number of legal responsibilities that, if neglected, can result in fines, penalties and legal disputes. Both the IRS and the state and federal Departments of Labor closely monitor payroll-related activities. As a result, every employer must be aware of and comply with a specific set of obligations.
Here is a breakdown of the main responsibilities that any company with employees on its payroll must assume:
Tax withholding
As an employer, you must withhold from each employee's salary the corresponding taxes, among them:
- Federal Income Tax (Impuesto Federal sobre la renta).
- Social Security Tax6.2% of salary.
- Medicare (Medicare Tax)1.45% of salary.
- State and local taxesif applicable.
It is essential to calculate and withhold these taxes correctly each pay period.
2. Payment of employer contributions
In addition to withholdings, you must contribute your share to the:
- Social Security (additional 6.2%).
- Medicare (additional 1,45%).
- FUTA (Federal Unemployment Tax Act)Federal unemployment tax.
- SUTA (State Unemployment Tax Act)State unemployment tax.
These charges cannot be deducted from the employee's salary: are 100% employer's responsibility.
3. Filing forms with the IRS and other agencies
Among the main ones are:
- Form 941Quarterly withholding tax return.
- Form W-2Annual report for employees (due by January 31).
- Form W-3Annual summary that accompanies W-2s.
- Form 940FUTA Annual Report.
There are also periodic reports to state and, in some cases, local agencies.
4. Record keeping
By law, you must keep records for at least 4 years, including:
- Hours worked.
- Rest and meal times (depending on the state).
- Wages paid and deductions applied.
- Employee classification documentation.
This is not only necessary in the event of an audit, but also as a backup for labor claims or internal discrepancies.
5. Proper classification of workers
You must correctly determine whether an employee is a employee or independent contractor. An error in this classification may lead to:
- Retroactive payment of taxes.
- Penalties for evasion of payroll taxes.
- Labor lawsuits.
Compliance with legal payroll obligations is not optional. The federal government and the states make it a priority. The good news is that when everything is set up correctly from the beginning, management becomes much smoother and more secure..
At JJRB, we help companies not only comply, but also design payroll systems that are efficient, automated and fail-safeusing the most modern tools and adapted to each case. This way, you can focus on your business, while we take care of legal compliance.
Conclusions
Payroll management is much more than issuing payments on time. It is a combination of tax compliance, administrative control and organizational strategy. When handled with care, precision and vision, it becomes a powerful tool for building trust, operational stability and growth projection.
As we have seen throughout the article, the legal responsibilities of the U.S. employer are broad and complex. From proper tax withholding and payment to worker classification, form filing and record keeping, every detail counts. One mistake, no matter how small, can result in IRS fines, labor disputes or audits that halt the pace of business.
But the good news is that with the right support, payroll management does not have to be a burden. On the contrary, it can become an automated, transparent process aligned with your business goals. An efficient payroll system not only reduces risks, but also improves team morale, reinforces your reputation and gives you real control over one of the most sensitive areas of the business: human capital.
At JJRB, we've spent years helping companies of all sizes implement comprehensive payroll management solutions tailored to their needs, industry and budget. From initial setup to monthly compliance, we make sure everything runs smoothly, so you can focus on growing.
Because at the end of the day, paying well is just the beginning.
Managing payroll intelligently is what really builds a solid company.



